BloombergNEF Electric Vehicle Outlook 2024: Key Insights and Future Trends
The BloombergNEF Electric Vehicle Outlook 2024 report provides an in-depth analysis of the current state and future projections of the electric vehicle (EV) market.
- BloombergNEF Electric Vehicle Outlook 2024: Key Insights and Future Trends
- 1. Global EV Market Overview
- 2. Policy and Market Dynamics
- 3. Technological Advancements and Cost Trends
- 4. Commercial Vehicles and Buses
- 5. Global Passenger Vehicle Outlook
- 6. Impact on Oil and Electricity Demand
- 7. Battery Supply Chain and Material Demand
- 8. Regional Adoption and Market Differences
- 9. Technological Innovations and Competitive Pricing
- 10. Future Outlook and Scenarios
- 11. Electrification of Two- and Three-Wheeled Vehicles
- 12. Shared Mobility and Connectivity
- 13. Plug-In Hybrid Vehicles (PHEVs)
- 14. Impact on Oil Demand and Road Fuel Consumption
- 15. Investment in Charging Infrastructure
- Conclusion
This comprehensive summary highlights key findings from the report, exploring global market trends, policy impacts, technological advancements, and regional adoption differences. By synthesizing these insights, this article aims to inform readers about the critical factors shaping the future of electric mobility and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Summary of BloombergNEF Electric Vehicle Outlook 2024
1. Global EV Market Overview
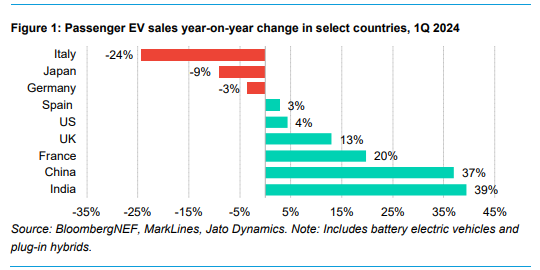
The 2024 outlook reveals varying paces of electric vehicle (EV) market growth worldwide. While global EV sales continue to rise, some markets are experiencing slowdowns. Developing economies, such as Thailand, India, Turkey, and Brazil, are seeing record sales due to low-cost models.
Chinese automakers are expanding rapidly into new markets, driven by the need to find new buyers.
Geopolitical tensions and protectionist measures, such as tariffs and efforts to onshore manufacturing, are impacting the pace of global EV adoption.
2. Policy and Market Dynamics
Policy support for EVs has become less certain, with several European countries reducing subsidies earlier than planned. This has led to a slowdown in sales and prompted calls to relax both near-term CO2 targets and the long-term plan to phase out internal combustion vehicles. In the US, progress will hinge on the outcome of the presidential election, while China remains a leader, having reached a point of consumer-driven EV sales growth.
The report highlights the importance of long-term goals to achieve net-zero emissions in road transport.
3. Technological Advancements and Cost Trends
Advances in battery technology have driven down costs significantly, with prices dropping by 90% over the past decade.
This trend is expected to continue, benefiting automakers and buyers but posing challenges for new entrants to the battery industry. Several next-generation battery technologies are nearing commercialization, promising further improvements in efficiency and cost. The introduction of lower-cost EV models is expected to drive increased adoption in the coming years.
4. Commercial Vehicles and Buses
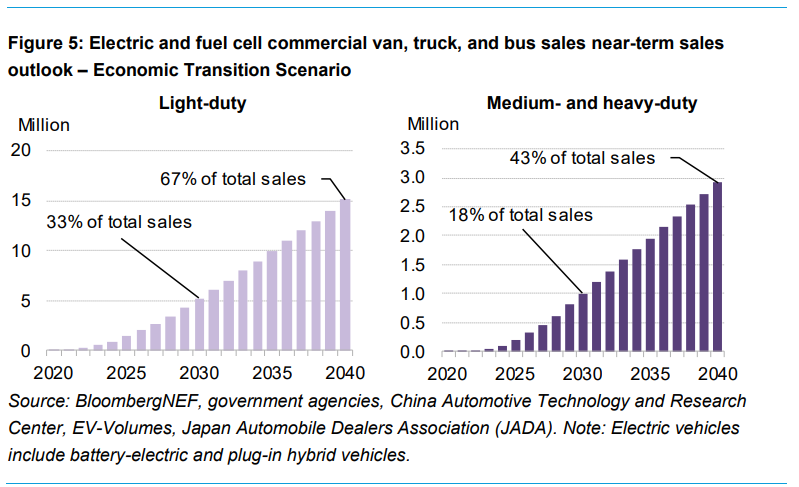
The commercial vehicle segment, including vans, trucks, and buses, is rapidly electrifying, particularly in China, South Korea, and Europe. Electric heavy trucks are expected to become economically viable for most use cases by 2030. Municipal buses are on track to exceed 60% electrification by that year, with electric light-duty delivery vans and trucks also seeing significant growth. The adoption of zero-emission powertrains is driven by both economic viability and new environmental policies.
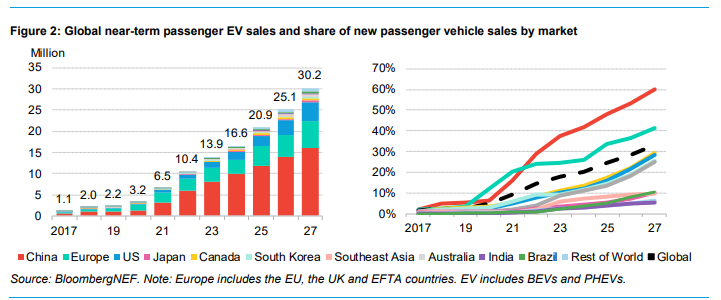
5. Global Passenger Vehicle Outlook
Despite a slowdown in growth rates, global passenger EV sales are expected to rise from 13.9 million in 2023 to over 30 million in 2027. By 2030, EVs are projected to account for 45% of global passenger vehicle sales. However, less than 50% of the global passenger-vehicle fleet is expected to be electric by 2040. The disparity in adoption rates between different regions underscores the need for continued policy support and technological advancement.
6. Impact on Oil and Electricity Demand
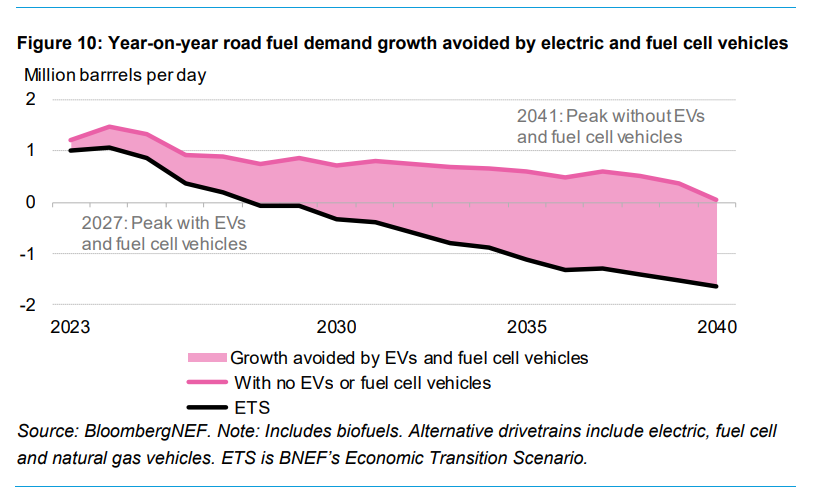
The increase in EVs and fuel-cell vehicles will displace significant oil demand, with road fuel demand peaking by 2027. By 2050, a fully electric global fleet could consume twice the amount of electricity the US did in 2023. This shift requires substantial investment in charging infrastructure and grid upgrades to accommodate the increased demand. Smart charging and variable pricing mechanisms will be essential to manage this demand effectively.
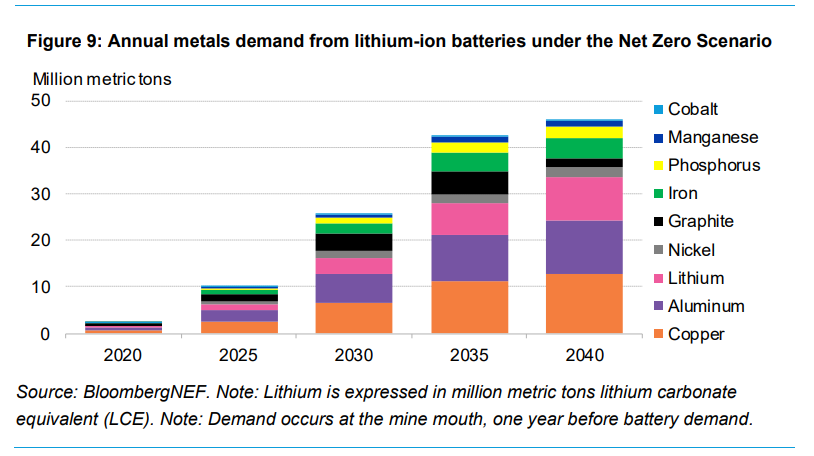
7. Battery Supply Chain and Material Demand
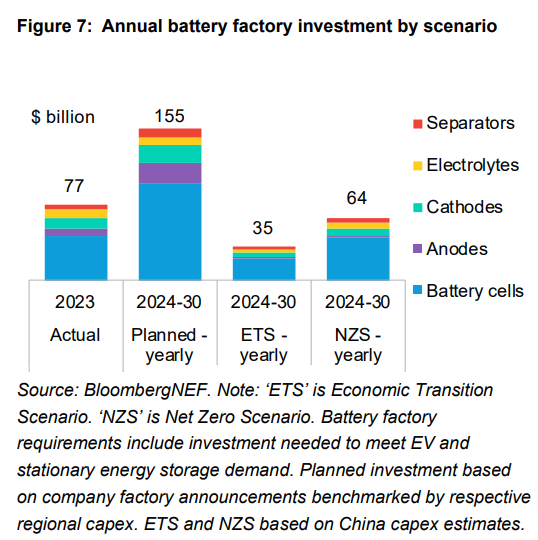
Large investments are needed across the battery supply chain. Annual lithium-battery demand is expected to reach 5.9 terawatt-hours by 2035. Over-investment in battery-cell manufacturing capacity is a concern, particularly in China, where planned capacity far exceeds demand. Recycling and new extraction technologies will be crucial to meet future material needs sustainably. The shift towards lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) batteries is reducing the demand for metals like nickel and manganese.
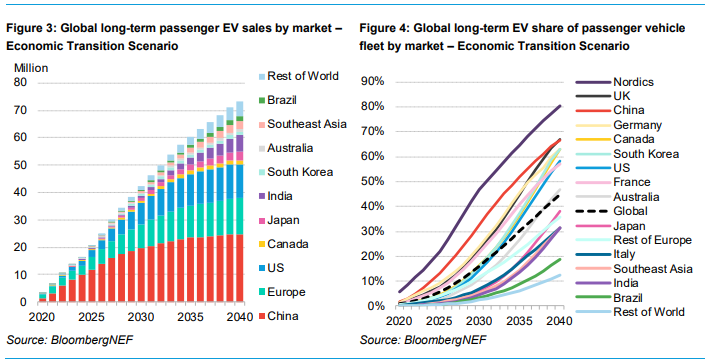
8. Regional Adoption and Market Differences
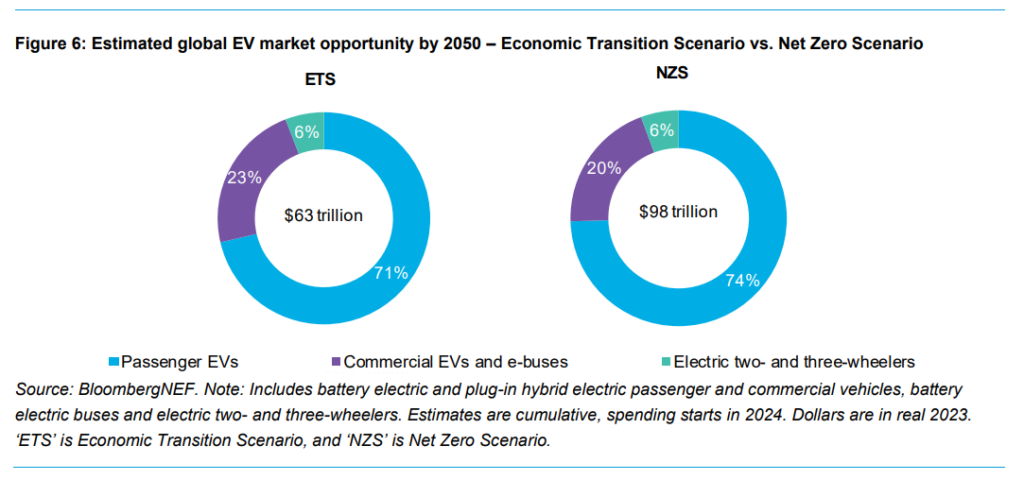
The EV adoption trajectory varies by region, with China and Europe leading the way. Emerging economies like Brazil and India are set to experience significant growth. However, regions like Southeast Asia, India, and Brazil will still be below the global average adoption by 2040 without stronger regulatory pushes. The report emphasizes the need for a stronger regulatory push in these regions to bridge the gap with more developed EV markets.
9. Technological Innovations and Competitive Pricing
Lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) batteries are gaining market share due to improvements in technology and competitive pricing, reducing the demand for metals like nickel and manganese. China’s dominance in low-cost battery production is driving global price reductions, posing challenges for international markets to compete. The report discusses the impact of China’s low-cost battery push on the global market and highlights the benefits and challenges associated with this trend.
10. Future Outlook and Scenarios
BloombergNEF provides two scenarios for the future of road transport: the Economic Transition Scenario and the Net Zero Scenario. The former describes expected trends based on current technological and economic conditions, while the latter outlines a path to achieving a zero-emission global road fleet by 2050. Both scenarios emphasize the need for sustained policy support and technological innovation to achieve long-term climate goals. The Economic Transition Scenario projects significant growth in EV sales, while the Net Zero Scenario requires more aggressive policy interventions to achieve a completely zero-emission vehicle fleet by 2050.
11. Electrification of Two- and Three-Wheeled Vehicles
Electrification is advancing rapidly in the two- and three-wheeled vehicle segments, particularly in emerging economies. Electric two-wheelers are set to reach 90% of global sales by 2040, while three-wheelers are already on track to achieve a zero-emission fleet by 2050. These segments are crucial for reducing emissions in densely populated urban areas where such vehicles are predominantly used.
12. Shared Mobility and Connectivity
Shared mobility solutions, vehicle connectivity, and autonomous driving technologies are expected to reshape automotive and freight markets. These innovations will complement the electrification of transport, offering additional benefits such as reduced traffic congestion and lower emissions.
13. Plug-In Hybrid Vehicles (PHEVs)
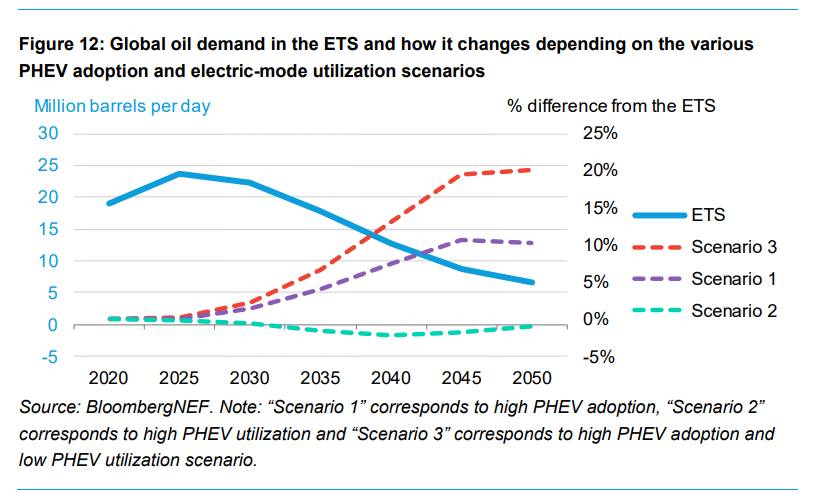
Plug-in hybrids are experiencing a resurgence, driven by increasing electric ranges and consumer interest. However, their role in the transition to zero-emission vehicles is debated, as they still rely on fossil fuels for part of their operation. The average electric range of PHEVs has increased, particularly in China, where some models exceed 100km.
14. Impact on Oil Demand and Road Fuel Consumption
With the rapid uptake of EVs and fuel-cell vehicles, oil demand from road transport is expected to peak by 2027. This will result in significant reductions in road fuel consumption, contributing to global efforts to mitigate climate change. The report projects that without EVs, road fuel consumption would continue to grow until 2041.
15. Investment in Charging Infrastructure
The transition to electric mobility requires substantial investment in charging infrastructure. Between $1.6 trillion and $2.5 trillion in cumulative investment is needed by 2050 to support the global EV fleet. The development of smart charging solutions and the expansion of fast-charging networks will be critical to meeting this demand.
Conclusion
The BloombergNEF Electric Vehicle Outlook 2024 underscores the dynamic and rapidly evolving nature of the global EV market. While significant progress has been made, particularly in reducing costs and increasing adoption, challenges remain. Regional disparities in policy support and market readiness, alongside geopolitical tensions and supply chain issues, highlight the complexity of the transition to electric mobility. However, with continued innovation and strategic policy interventions, the vision of a sustainable, zero-emission transport system by 2050 remains achievable.




