How NMC Lost Market Share to LFP in the Last 3 Years
In recent years, the electric vehicle (EV) market has witnessed significant shifts in battery technology preferences. One of the most notable changes has been the dramatic rise of Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries at the expense of Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) batteries.
Understanding this transition is crucial for stakeholders in the EV industry, as it reflects broader trends in battery technology, cost efficiency, and regulatory policies.
Let’s delve into how NMC lost market share to LFP in the past three years, drawing insights from the trends observed in China’s EV battery market from 2016 to 2022.
The Rise of LFP and Decline of NMC
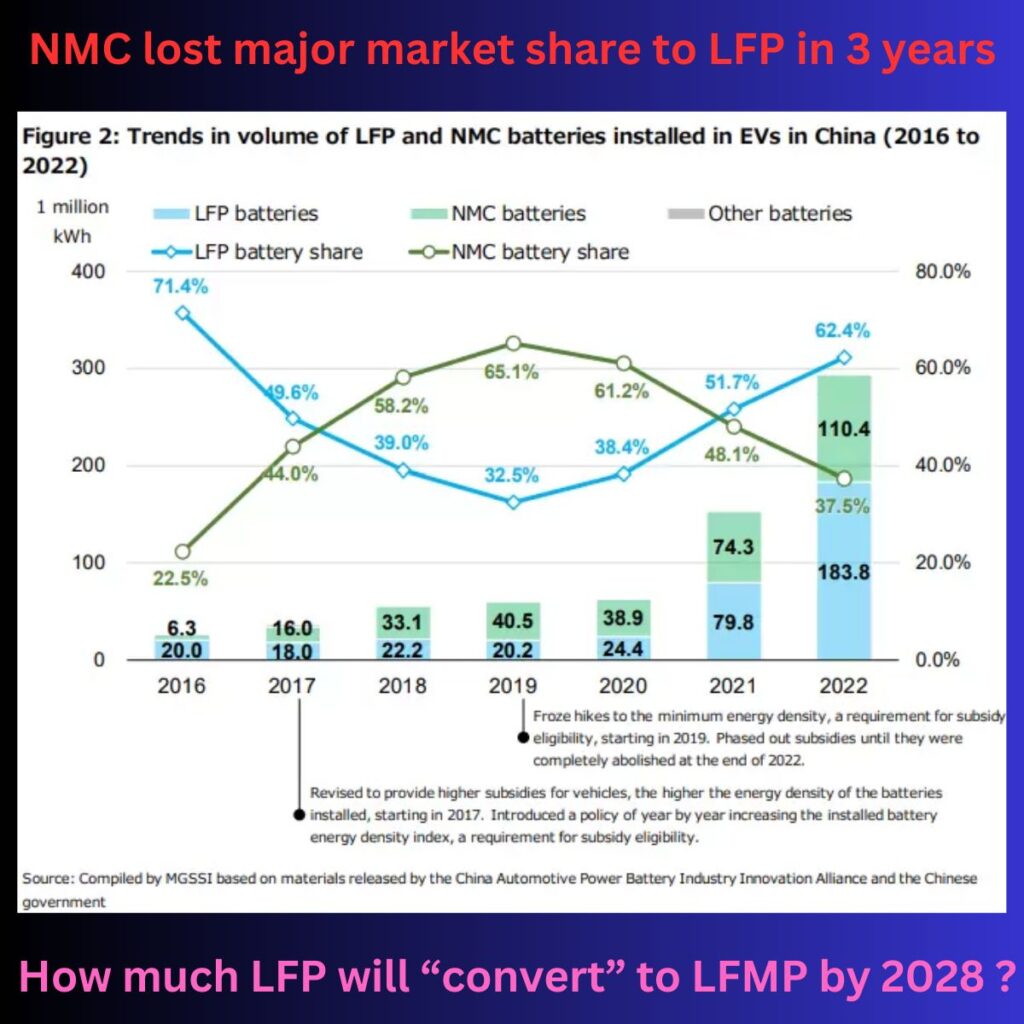
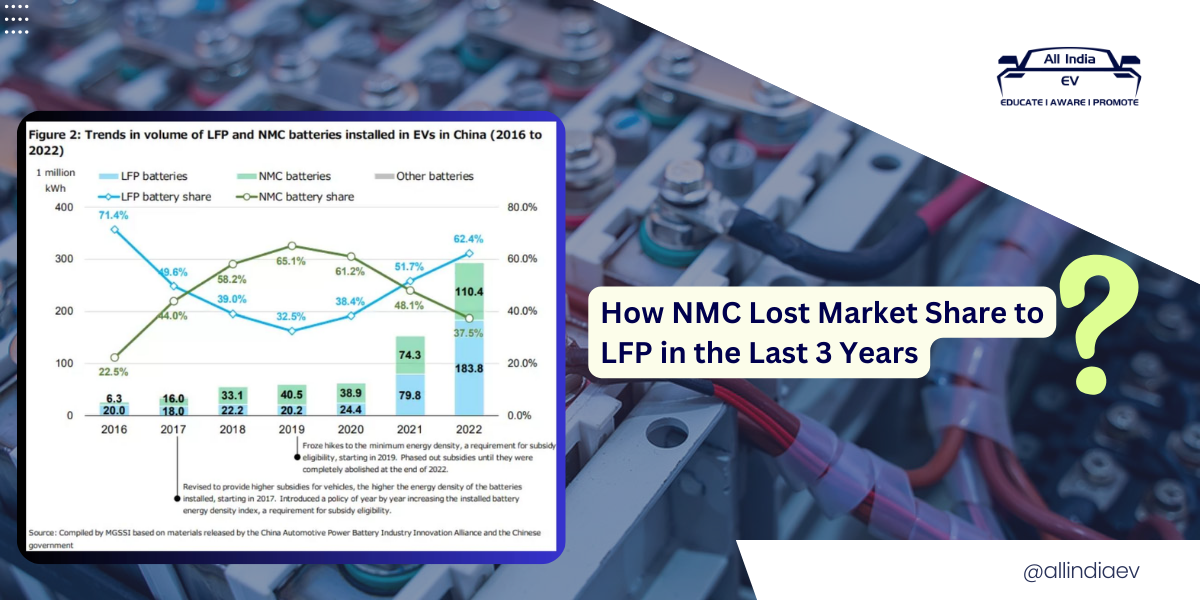
The graph from the China Automotive Power Battery Industry Innovation Alliance provides a clear depiction of the shifting dynamics between LFP and NMC batteries from 2016 to 2022.
In 2019, NMC batteries held a commanding 65.1% share of the market, while LFP batteries were at a mere 32.5%. However, by 2022, this scenario had reversed drastically, with LFP batteries surging to 62.4% and NMC batteries plummeting to 37.5%.
Cost Efficiency
LFP batteries are known for their lower cost compared to NMC batteries. The primary reason is the cheaper raw materials used in LFP batteries, which do not rely on cobalt—a costly and geopolitically sensitive material. This cost advantage has made LFP batteries more attractive, especially in price-sensitive markets like China. Consequently, this cost efficiency has significantly contributed to NMC losing market share to LFP.
Safety and Longevity
LFP batteries offer superior thermal stability and safety. They are less prone to overheating and have a longer lifecycle compared to NMC batteries. As EV adoption grows, consumers and manufacturers alike are prioritizing these attributes, leading to a preference for LFP technology. This focus on safety and longevity has been a key factor in NMC losing market share to LFP.
Policy and Regulation
China’s regulatory environment has played a pivotal role. Starting in 2017, China revised its subsidy policies to favor batteries with higher energy density, indirectly benefitting NMC batteries initially. However, as these subsidies were phased out by the end of 2022, the market dynamics shifted in favor of LFP batteries, which began to dominate due to their inherent cost and safety advantages. These regulatory changes have been instrumental in NMC losing market share to LFP.
Data Insights: A Closer Look
▶️ 2019: NMC batteries had a significant lead with 65.1% of the market, while LFP batteries held 32.5%. The total volume of NMC batteries installed was 40.5 million kWh, compared to 22.2 million kWh for LFP batteries.
▶️ 2020: The gap started to narrow, with NMC holding 61.2% and LFP climbing to 38.4%.
▶️ 2021: A pivotal year where LFP batteries overtook NMC in volume (74.3 million kWh vs. 79.8 million kWh), despite NMC still holding a majority share at 51.7%.
▶️ 2022: LFP batteries surged ahead, capturing 62.4% of the market with 183.8 million kWh installed, while NMC dropped to 37.5% with 110.4 million kWh.
This data underscores the rapid acceleration of LFP battery adoption and the corresponding decline of NMC batteries in the market. These trends clearly illustrate how NMC lost market share to LFP.
The Future Outlook: LFP and LFMP
Looking ahead to 2028, the question arises: how much LFP will convert to LFMP (Lithium Iron Manganese Phosphate)? LFMP represents an evolution in LFP technology, promising enhanced energy density while retaining the cost and safety benefits.
As the industry continues to innovate, LFMP could become a significant player, potentially transforming a portion of the LFP market. Predictions suggest that by 2028, a considerable fraction of the current LFP market could transition to LFMP, driven by the ongoing quest for higher performance and efficiency in EV batteries. The exact extent of this conversion will depend on technological advancements, cost considerations, and regulatory influences.
The shift from NMC to LFP batteries in the last three years highlights the dynamic nature of the EV battery market. Driven by cost efficiency, safety, and evolving policies, LFP batteries have emerged as a dominant force. As we look to the future, the potential rise of LFMP technology adds another layer of excitement and anticipation. For stakeholders in the EV industry, staying attuned to these trends is essential for navigating the rapidly changing landscape of battery technology.




