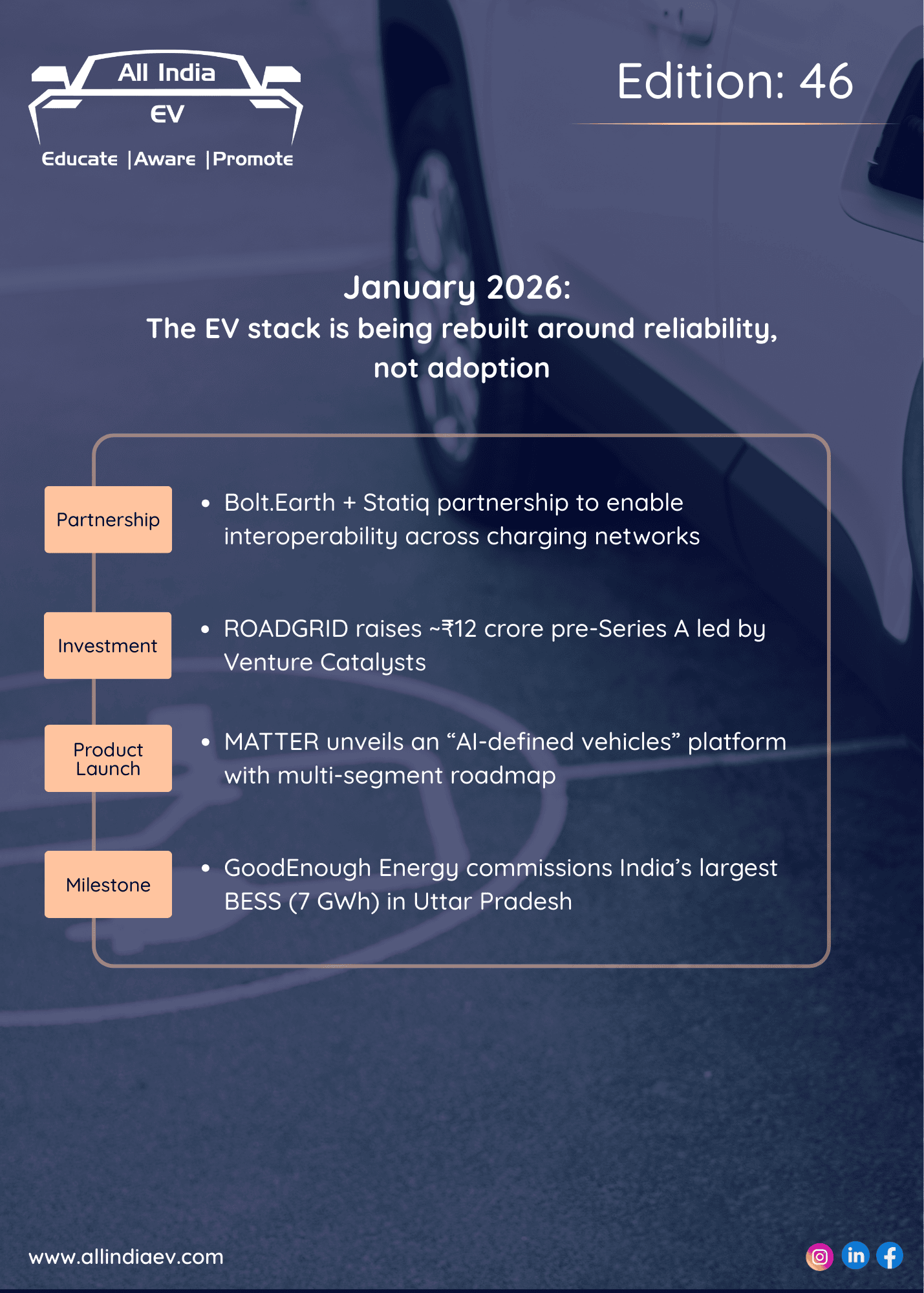
As the electric vehicle (EV) industry grows, simplifying the charging experience becomes critical for widespread adoption. Two leading technologies—Autocharge and Plug & Charge—have emerged to address this need. While both aim to make EV charging more seamless, they differ in technology, security, cost, and user experience. This article delves into what Autocharge and Plug & Charge are, how they work, and their key differences, supported by data and industry insights.
What is Autocharge?
Autocharge is a streamlined EV charging technology that enables drivers to initiate charging automatically without manual authentication. It works with vehicles and chargers equipped with the Combined Charging System (CCS), a widely adopted standard.
How Autocharge Works
- Connection: The EV communicates its unique identifier—like a Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) or Media Access Control (MAC) address—to the charging station upon connection.
- Authentication: The identifier is verified against a pre-registered database maintained by the Charging Station Management System (CSMS).
- Seamless Charging: Once authorized, charging begins automatically without the need for apps, RFID cards, or PIN codes.
Key Features of Autocharge
- Convenience: Eliminates manual steps, providing an intuitive experience.
- Compatibility: Supports CCS connectors, which are used by over 70% of EVs globally, according to a 2023 report by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- Efficiency: Background processes like authentication and billing occur automatically, reducing wait ti
What is Plug & Charge?
Plug & Charge is an advanced EV charging technology that simplifies charging and payment by securely automating the entire process. Based on the ISO 15118 standard, it ensures seamless interoperability across EVs and charging networks.
How Plug & Charge Works
- Secure Connection: The EV and charging station initiate a secure digital handshake upon connection.
- Authentication: The vehicle’s unique digital certificate, stored like a digital wallet, is verified by the charging network.
- Automatic Billing: Payments are processed automatically based on pre-registered billing information.
- Enhanced Security: Uses encryption to protect user data and ensure secure transactions.
Key Features of Plug & Charge
- ISO 15118 Standardization: Supports unified communication and payment systems.
- Enhanced Security: Employs cryptographic methods for secure data exchange.
- Interoperability: Designed for use across various EV brands and charger types.
- User-Friendly Payments: Transactions are automatic, eliminating the need for external payment methods
Key Differences Between Autocharge and Plug & Charge
| Feature | Autocharge | Plug & Charge |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | DIN SPEC 70121 | ISO 15118 |
| Authentication | VIN/MAC-based | Digital certificate-based |
| Security | Basic | Advanced encryption |
| Infrastructure Cost | Low | High |
| Compatibility | Limited to CCS chargers | Broad adoption expected |
| User Experience | Fast initiation | Seamless but slightly slower setup |
| Adoption Rate | Moderate | Increasing as ISO 15118 gains traction |
Security and Protocols
Plug & Charge leverages ISO 15118, ensuring secure communication via encryption and digital certificates. In contrast, Autocharge uses simpler protocols like DIN SPEC 70121, offering basic security comparable to RFID cards.
Cost Implications
Implementing Plug & Charge requires significant infrastructure upgrades to meet ISO 15118 standards, leading to higher costs. Autocharge, being simpler, is more cost-effective and can integrate into existing systems with minimal changes.
Real-World Adoption and Trends
- Plug & Charge: Supported by major automakers like Tesla, Ford, and Volkswagen, Plug & Charge is gaining traction. By 2023, over 25% of new EV models featured ISO 15118 compatibility, and the number is expected to reach 60% by 2025, according to BloombergNEF.
- Autocharge: Widely used in Europe, particularly by EV fleets, due to its cost-effectiveness and compatibility with existing CCS chargers. A study by EVBox found that 40% of CCS-based chargers support Autocharge globally.
Which Technology is Better?
The choice between Autocharge and Plug & Charge depends on user priorities:
- For Security and Interoperability: Plug & Charge is ideal for those seeking advanced security and a unified charging experience.
- For Simplicity and Speed: Autocharge provides a faster and more straightforward solution, especially for EV fleets.
The Road Ahead
Both Autocharge and Plug & Charge represent significant advancements in EV charging technology. Plug & Charge, with its focus on standardization and security, is poised to dominate the EV market as ISO 15118 adoption grows. Meanwhile, Autocharge remains a practical choice for networks seeking cost-effective solutions.
As EV adoption accelerates—projected to account for 45% of global vehicle sales by 2030, according to the IEA—streamlined charging technologies like these will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of sustainable transportation.
While both technologies make EV charging more user-friendly, the choice ultimately depends on factors like security, infrastructure costs, and user preferences. Whether through the simplicity of Autocharge or the advanced features of Plug & Charge, the future of EV charging is undoubtedly more convenient and efficient.